mysql tutorial for beginners (8/8) : Backing up & Restoring MySQL data HD
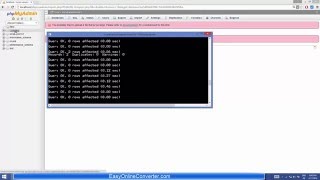
mysql tutorial for beginners (8/8) : Backing up & Restoring MySQL data Backing up and restoring MySQL data is easy with the mysqldump command With mysqldump, you can dump a database or collection of databases into one or more files containing all the instructions necessary to re-create all your tables and repopulate them with your data. It can also generate files in CSV or XML format. Its main drawback is that you must make sure that no one writes to a table while you’re backing it up. There are various ways to do this, but the easiest is to shut down the MySQL Server before mysqldump and start up the server again after mysqldump finishes. Or you can lock the tables you are backing up before running mysqldump. To ensures that MySQL remains running for read purposes, but writes cannot be made then issue this command: LOCK TABLES grade_per_question READ, question_in_test READ, questions READ, students READ, tests READ; However, before you can dump the contents of a database, you must make sure that mysqldump is in your path In Tag u, specify the username and in tag p specify the password Then enter the database name you want to dump Mysqldump –u Safaa –p examSystem; By default the output from mysqldump is simply printed out, but you can capture it in a file through the redirect symbol (greater than symbol) Assuming that you wish to call the backup file ExaminationSystem.sql Mysqldump –u Safaa –p examSystem ExaminationSystem.sql This code can be used to restore a database from a backup, even if it currently exists, because it will first drop any tables that need to be re-created thus avoiding potential MySQL errors. To back up only a single table from a database, Just write down the table name after the database name If you want to back up all your MySQL databases at once you can use the option –all-databases Mysqldump –u root –all-databases all_databases.sql To Perform a restore from a file, call the mysql executable Then provide the necessary credentials, From using the less than symbol pass it the file to restore Mysql –u root all_databases.sql To restore a single database, use the –D option followed by the name of the database, Mysql –u Safaa –p –D examSystem all_databases.sql To restore a single table to a database, use the following command Mysql –u Safaa –p –D examSystem students.sql Finally, to release the locks enter the following: UNLOCK TABLES; This is the end of mysql tutorial for beginners series, now you are not a beginner anymore go ahead and dig deep into mysql, I wish you the best and success, Good luck Subscribe for more: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- https://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=saf3al2a SWE.Safaa Al-Hayali - saf3al2a
Похожие видео
Показать еще
 HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD
 HD
HD

 HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD


 HD
HD HD
HD
 HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD HD
HD